Biodegradable Plate Stats for Smart Shoppers

I choose a biodegradable plate when I want to help reduce waste. These plates come from renewable resources. They break down within a few months. Many brands earn compostable certification. I find these plates strong and safe for serving food. I trust them for durability and sustainability.
- 🌱 Made from renewable materials
- 🕒 Decompose within months
- ✅ Certified compostable
Key Takeaways
- Biodegradable plates made from materials like bagasse, bamboo, and PLA break down much faster than plastic, reducing landfill waste and environmental impact.
- Choosing certified biodegradable plates ensures safety, durability, and proper composting, whether at home or in industrial facilities.
- Buying biodegradable plates in bulk lowers costs and supports sustainability by reducing packaging and shipping waste.
Biodegradable Plate Materials and Decomposition Stats

Common Materials Used
When I shop for a biodegradable plate, I look for products made from renewable resources. The most common materials I see include:
- Bagasse: This is a fiber left after extracting juice from sugarcane. It feels sturdy and holds up well with hot foods.
- Bamboo: Plates made from bamboo offer a natural look and strong structure. Bamboo grows quickly, making it a sustainable choice.
- PLA (Polylactic Acid): PLA comes from fermented corn starch. It looks and feels like plastic, but it is plant-based and compostable under the right conditions.
Each material brings its own benefits. I notice that bagasse and bamboo plates often feel more natural and break down faster than PLA options.
Decomposition Rates and Compostability
I always check how fast a biodegradable plate will break down. In my experience, plates made from a mix of bamboo and bagasse can biodegrade in about 60 days under natural conditions. This is much faster than regular plastic plates, which can last for hundreds of years.
PLA plates need special composting conditions. They do not break down easily in a home compost pile. Industrial composting facilities use higher temperatures and better aeration, which help PLA plates decompose in a few weeks to a few months. At home, composting takes longer—sometimes up to a year—and may not fully break down tougher materials.
Tip: Always check if your biodegradable plate is certified for home or industrial composting. This helps you dispose of it in the most eco-friendly way.
| Aspect | Home Composting | Industrial Composting |
|---|---|---|
| Decomposition Time | 6-12 months | Few weeks to months |
| Conditions | Variable | Optimized |
| Material Compatibility | Simpler materials | Tougher items, like PLA |
Biodegradable Plate Environmental Impact and Performance

Landfill Reduction and Carbon Footprint
When I choose a biodegradable plate, I know I am making a positive impact on the environment. These plates break down much faster than traditional plastic or foam options. I see less waste piling up in landfills because biodegradable materials decompose within months, not centuries. This quick breakdown means less space taken up by trash and fewer harmful emissions released over time.
I also pay attention to the carbon footprint. Manufacturing a biodegradable plate often uses less energy and produces fewer greenhouse gases compared to plastic plates. For example, bagasse and bamboo plates come from renewable resources that absorb carbon dioxide as they grow. When I use these plates, I help reduce the demand for fossil fuels and lower the overall carbon footprint of my meals.
However, I have learned that some biodegradable plates contain additives to improve their performance. These additives can affect both the environment and food safety. Here is a table that shows the most common additives and their safety concerns:
| Additive Type | Number Identified | Examples | Safety Concerns |
|---|---|---|---|
| Slip Agents | 58 | Palmitamide | Some slip agents classified as highest risk (RISK I), indicating potential safety concerns |
| Antistatic Agents | 27 | N/A | Not specifically highlighted as high risk, but part of overall migrants |
| Antioxidants | 22 | Degradation products such as bis(2,4-di-tert-butylphenyl) phosphonate, 7,9-di-tert-butyl-1-oxaspiro[4.5]deca-6,9-diene-2,8-dione | Some antioxidant degradation products classified as highest risk (RISK I) |
| Plasticizers | N/A | Triisobutyl phosphate | Some plasticizers also classified as highest risk (RISK I) |
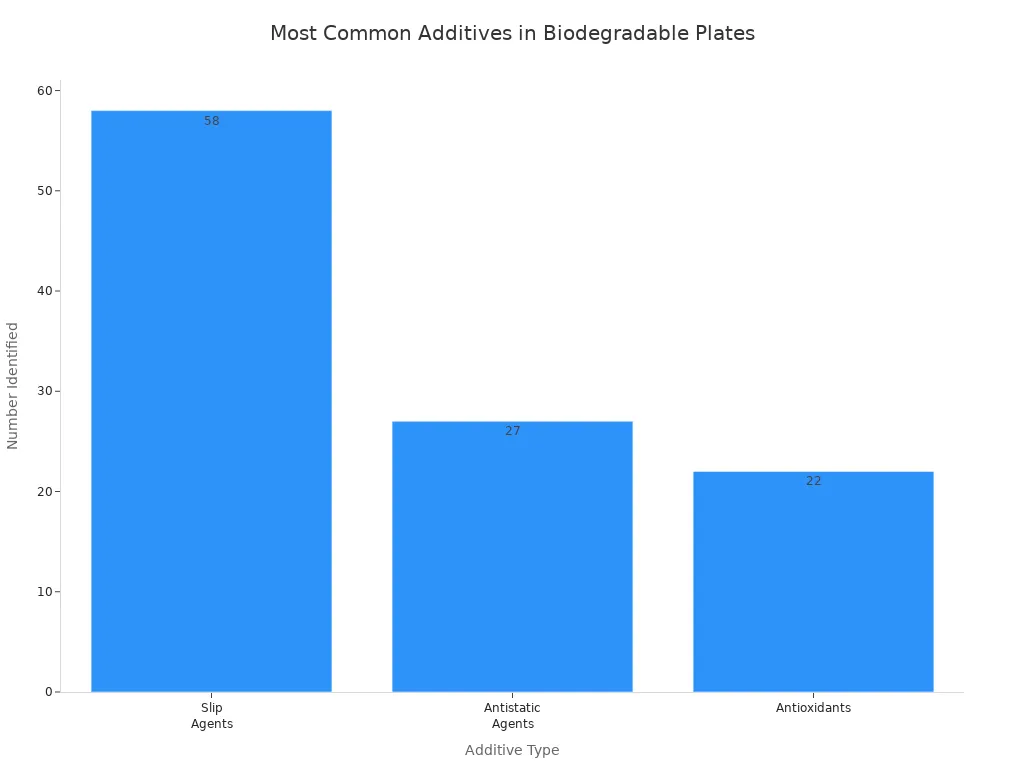
Note: While these additives help improve the strength and usability of biodegradable plates, some may pose safety risks for food contact. I always look for products with clear safety certifications and transparent ingredient lists.
Strength, Heat Resistance, and Usability
I expect my plates to handle a variety of foods, from hot soups to cold desserts. In my experience, a biodegradable plate made from bagasse or bamboo performs well in both hot and cold food applications. I have used these plates at picnics, parties, and even large events, and they never let me down.
- Bagasse plates hold hot soups and cold desserts without bending or leaking.
- They resist heat and stay sturdy at typical serving temperatures.
- I do not worry about harmful chemicals like BPA or phthalates, which are sometimes found in plastic plates.
- At a recent event with over 500 guests, I noticed that bagasse plates stayed strong and composted fully within 90 to 180 days.
- Plastic plates do not break down and may release toxins, while Paper Plates often feel flimsy and cannot handle hot foods as well.
- I find that biodegradable bagasse plates offer a reliable, sustainable, and safe alternative for any meal.
Tip: For the best results, I always check if the plate is certified for food contact and compostability. This ensures both safety and performance.
Biodegradable Plate Cost, Value, and Certifications
Price Comparison and Cost-Effectiveness
When I compare the cost of a biodegradable plate to traditional options, I notice that prices can be higher for eco-friendly choices. However, I find that bulk purchasing makes a big difference. Buying large quantities lowers the price per plate, which helps businesses and event organizers save money. I often see that ordering directly from manufacturers or distributors brings even more savings than buying from retailers. Bulk orders also mean fewer shipments and less packaging waste, which supports my goal of reducing environmental impact. I always check for minimum order requirements and consider storage space before making a large purchase.
- Bulk buying reduces cost per plate.
- Direct orders from manufacturers offer better deals.
- Fewer shipments mean less packaging waste.
- I plan for storage and shipping costs when ordering in bulk.
Lifespan and Durability
Durability matters to me when I serve food at events. Some users complain that plant fiber plates feel flimsy, especially with heavy or wet foods. I have experienced this with certain brands. Bamboo plates stand out as a strong alternative. They resist heat and moisture, so I can serve both hot and cold dishes without worrying about leaks or sagging. Manufacturers choose bamboo for its natural strength, which means they do not need to add chemical coatings that could affect compostability. I also appreciate that bamboo grows quickly and needs less water, making it a sustainable and reliable choice.
Certifications and Standards
I always look for certifications when I buy biodegradable plates. These labels show that the product meets strict compostability and safety standards. Here is a table that summarizes the most recognized certifications and what they mean:
| Certification Name | Description & Criteria |
|---|---|
| BPI Certified Compostable | Certification for industrial compostability, ensuring products break down safely in commercial composting. |
| TÜV Austria OK compost HOME & INDUSTRIAL | European certifications based on EN 13432 standard requiring disintegration within 12 weeks and biodegradation within 6 months. |
| Compost Manufacturing Alliance (CMA) Certified | Combines lab and field tests to verify compliance with ASTM standards; replaced Cedar Grove certification. |
| ASTM D6400 | US standard requiring biodegradation within 180 days, non-toxicity, and organic compound yield. |
| ASTM D6868 | Standard for compostability of plastic films or coatings on compostable products. |
| DEBIO Certified | Norwegian certification ensuring products can be used in organic agriculture after composting. |
| CAN/BNQ 0017-088 | Canadian standard ensuring compostability without negatively affecting compost quality. |
| Seedling Logo | European third-party certification indicating compliance with EN 13432, authorized by TÜV Austria. |
Tip: I always check for these certifications to make sure my biodegradable plate choice meets compostability and safety standards.
I always choose a biodegradable plate for its eco-friendly benefits and dependable performance. These plates help me reduce waste and support sustainability. When I shop, I look for certified, durable options that fit my needs.
Smart shoppers check certifications and compostability before buying.
FAQ
Are biodegradable plates safe for hot foods?
I always use biodegradable plates for hot meals. They resist heat well and do not release harmful chemicals. I trust certified brands for food safety.
Can I compost biodegradable plates at home?
I check the packaging for home compost certification. Some plates break down in my backyard compost, but others need industrial facilities. I always follow disposal instructions.
How do I know if a plate is truly biodegradable?
I look for certifications like BPI or TÜV Austria.
Certified logos on packaging give me confidence in the product’s compostability and safety.










